
Life insurance is a contract between a life insurance company and a policyholder. A life insurance policy promises that when the insured person dies, the insurer will pay an amount of money to one or more named beneficiaries in exchange for the policyholder’s lifetime premiums.h
Types of Life Insurance
Many different types of life insurance are available to satisfy a wide range of needs and preferences. Depending on the person’s short- or long-term demands, the major decision of whether to purchase temporary or permanent life insurance is critical.
1. Term life insurance
Term life insurance is designed to last a set number of years and then expire. When you buy the policy, you get to choose the duration. Common terms include ten, twenty, and thirty years. The finest term life insurance policies strike a mix between affordability and long-term financial strength.
Insurance Information Institute. “What are the Different Types of Term Life Insurance Policies?”
- Decreasing term life insurance is renewable term life insurance with coverage decreasing over the life of the policy at a predetermined rate.
- Convertible term life insurance allows policyholders to convert a term policy to permanent insurance.
- Renewable term life insurance provides a quote for the year the policy is purchased. Premiums increase annually and are usually the least expensive term insurance in the beginning.
After the term, many term life insurance policies offer yearly renewal. Although this can extend your life insurance coverage, the renewal rate is depending on your age, so premiums might skyrocket each year. Term life insurance conversion is a better permanent coverage option. Not all term life policies offer this; look for a convertible term policy if you care.
2. Permanent Life Insurance
Permanent life insurance lasts forever unless the policyholder stops paying or surrenders it. Late premium payments can trigger automatic premium loans in some policies. It costs more than term.
Insurance Information Institute. “What are the Different Types of Permanent Life Insurance Policies?”
- Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance. It accumulates a cash value in order to last the lifetime of the insured person. Cash-value life insurance also allows the policyholder to use the cash value for many purposes, such as a source of loans or cash or to pay policy premiums.
- Universal life (UL) insurance is a type of permanent life insurance with a cash value component that earns interest. Universal life features flexible premiums. Unlike term and whole life, the premiums can be adjusted over time and designed with a level death benefit or an increasing death benefit.
- Indexed universal life (IUL) is a type of universal life insurance that lets the policyholder earn a fixed or equity-indexed rate of return on the cash value component.
- Variable universal life (VUL) insurance allows the policyholder to invest the policy’s cash value in an available separate account. It also has flexible premiums and can be designed with a level death benefit or an increasing death benefit.
Top-Rated Companies to Compare
When shopping for insurance, consider starting with our list of the finest life insurance companies, some of which are included below:
| Company | AM Best Rating | Coverage Capacity | Maximum Issue Age | Policies Offered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nationwide Best Overall Compare Quotes on BestMoney | A+ | Over $5 million | 85 | Term, whole, UL, IUL, VUL, final expense |
| Protective Best for Term Compare Quotes on BestMoney | A+ | Over $5 million | 85 | Term, whole, UL, IUL, VUL |
| MassMutual Best Convertible Term Life Compare Quotes on BestMoney | A++ | Over $5 million | 90 | Term, whole, UL, VUL |
| Mutual of Omaha Best Return-of-Premium Term Compare Quotes on BestMoney | A+ | Over $5 million | 85 | Term, UL, IUL, final expense |
| Guardian Great Traditional Insurer Compare Quotes on BestMoney | A++ | Over $5 million | 90 | Term, whole, UL, VUL |
| USAA Best for Military Compare Quotes on BestMoney | A++ | Over $5 million | 85 | Term, whole, UL |
| New York Life Best Whole Life Compare Quotes on BestMoney | A++ | Over $5 million | 90 | Term, whole, UL, VUL |
Term vs. Permanent Life Insurance
Term life insurance is unlike permanent life insurance in various respects yet best suits most people seeking affordable life insurance. Term life insurance pays a death payment if the policyholder dies before the term ends. Life insurance remains permanent if the policyholder pays the premium. Term life premiums are less than permanent life since it doesn’t create cash value.
You should assess your finances and estimate how much money is needed to maintain your beneficiaries’ level of living or meet your requirement before applying for life insurance. Consider how long you’ll need coverage.
If you are the main parent of two 2- and 4-year-olds, you need enough insurance to cover your custodial duties until they can support themselves.
You may examine the cost of a nanny, housekeeper, or commercial child care and cleaning services, then add education costs. Consider your spouse’s mortgage and retirement expenses when calculating life insurance. Especially if the spouse brings in little or stays home. The death benefit you might buy—if you can afford it—is the sum of these expenditures over the next 16 years, plus inflation.
What Affects Your Life Insurance Premiums and Costs?
Many things affect life insurance premiums. Some factors are out of your control, but others can be addressed to lower the cost before and after applying. Life insurance costs depend primarily on your health and age, so buying it early is ideal.
After being approved for insurance, you can request a risk class change if your health has improved and you’ve made beneficial lifestyle adjustments. Even if your health worsens after underwriting, your premiums won’t rise. Better health may lower your premiums. Additional coverage may be cheaper than before.
Life Insurance Buying Guide
Step 1: Determine How Much You Need
Consider what expenses will need to be addressed in the case of your death. Things include mortgages, college tuition, and other debts, not to mention burial costs. Furthermore, income replacement is an important consideration if your spouse or loved ones require cash flow but are unable to offer it on their own.
There are helpful tools available online for calculating the lump payment required to cover any prospective expenses.
Step 2: Prepare Your Application
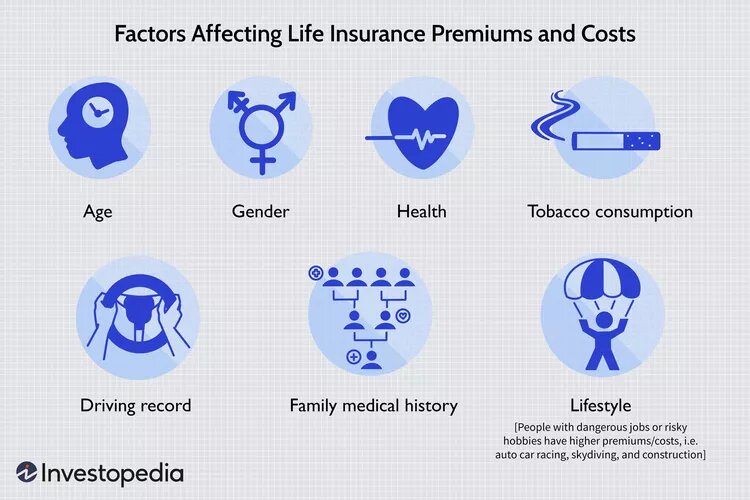
In most cases, life insurance applications involve personal and family medical history, as well as beneficiary information. You may be required to have a medical examination and reveal any preexisting medical conditions, a history of traffic offenses, DUIs, and any dangerous hobbies, such as vehicle racing or skydiving. The following are essential components of most life insurance applications:
- Age: This is the most important factor because life expectancy is the biggest determinant of risk for the insurance company.
- Gender: Because women statistically live longer, they generally pay lower rates than males of the same age.
Smoking: A person who smokes is at risk for many health issues that could shorten life and increase risk-based premiums. - Health: Medical exams for most policies include screening for health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer and related medical metrics that can indicate risk.
- Lifestyle: Dangerous lifestyles can make premiums much more expensive.
- Family medical history: If you have evidence of major disease in your immediate family, your risk of developing certain conditions is much higher.
- Driving record: A history of moving violations or drunk driving can dramatically increase the cost of insurance premiums.
Standard types of identification will also be required before a policy can be established, such as your Social Security card, driver’s license, or U.S. passport.
Step 3: Compare Policy Quotes
After collecting all your information, you can compare life insurance rates from different companies. It’s crucial to choose the best policy, company rating, and premium cost because prices vary widely. Finding the right life insurance policy might save you a lot of money since you’ll pay it regularly for decades.
Benefits of Life Insurance
Most people purchase life insurance to help beneficiaries who would suffer financially when the insured dies. However, life insurance’s tax advantages—tax-deferred cash value growth, tax-free dividends, and tax-free death benefits—can offer affluent individuals strategic alternatives. Life insurance has several benefits.:
1. Life Insurance Can Cover Final Expenses: The primary benefit of including life insurance in your financial plan is that if you die, your heirs will get a lump sum, tax-free payout from the policy. They can utilize this money to cover your final expenses and replace your income.
Life insurance can also help you while you’re living. Some insurance pay out if you develop a chronic or terminal illness, while others provide money to help you retire. Depending on your policy, this could include covering funeral costs, medical bills, auto loans, paying off a mortgage, or a down payment for a new home.
2. Avoiding Taxes: The death benefit of life insurance is normally tax-free. Wealthy persons may get permanent life insurance in a trust to cover estate taxes. This technique protects estate worth for heirs. Tax avoidance is a legal way to reduce one’s tax bill, unlike tax evasion. Your beneficiaries don’t have to record life insurance payouts as income on their tax returns.
A beneficiary who chooses installment payout may get earned interest. Interest is taxed and must be reported. Estate taxes may be offset by life insurance payouts, depending on your state. Here, your heirs won’t have to liquidate assets or pay from their inheritance.
3. Your Dependents Will Have Money for Living Expenses: One rule of thumb is that life insurance death benefits should be 10 times income. Your dependents will still be able to pay their bills if you have a policy or policies that size. Policy benefits can cover crucial everyday expenses like rent or mortgage, utilities, and groceries.
Your financial goals and resources determine how much life insurance to buy. You may need extra for other important expenses. You want the insurance to pay for your kids’ college tuition so they don’t need student loans. If you have a lot of savings, a lesser life insurance coverage may be fine.
4. You Can Get Coverage for Chronic and Terminal Illnesses: Riders, or endorsements, are available from many life insurance carriers to enhance or adjust coverage. Accelerated benefits riders let you use your death benefit before you die. Some policies allow you can use your death benefit to pay for care or other expenditures if you have a terminal disease.
Long-term care (LTC) riders cover home health-care workers, long-term care facilities, and nursing home treatment not covered by regular health insurance. The insurance may pay a flat sum or a monthly portion of your death benefit (1% to 4%). Before using most LTC coverage riders, you must wait 90 days.
5. Policies Can Supplement Your Retirement Savings: Whole, universal, and variable life insurance policies can build cash value and provide death payments. The policy provider guarantees cash value growth. Market conditions do not effect growth, thus money build steadily. Additionally, entire life insurance cash value grows tax-deferred. No income taxes are paid on cash value or growth until it is withdrawn.
You can use the cash worth to buy a car or put down a mortgage as it grows. You can use it in retirement if needed. If you don’t surrender your policy, borrowing against your cash value is tax-free. However, the insurance company will charge interest on the loan until you repay it. The interest rates on these loans vary by insurer.
A life insurance policy shouldn’t replace a 401(k) or IRA. Cash value life insurance costs far more than term life insurance, which only pays a death benefit.
Who Needs Life Insurance?
Life insurance provides financial support to surviving dependents or other beneficiaries in the event of an insured policyholder’s death. Here are some instances of persons who could require life insurance:
- Parents with minor children. If a parent dies, the loss of their income or caregiving abilities may result in financial difficulty. Life insurance can ensure that the children have the necessary financial resources until they are able to sustain themselves.
- Parents with adult children who have special needs. Life insurance can ensure that children who require lifetime care and will never be self-sufficient are provided for after their parents die. The death benefit can be used to fund a special needs trust, which will be managed by a trustee for the benefit of the adult child.
“Liens, Adjustments and Recoveries, and Transfers of Assets.” - Adults who own property together. Married or not, if the death of one adult would mean that the other could no longer afford loan payments, upkeep, and taxes on the property, life insurance may be a good idea. One example would be an engaged couple who take out a joint mortgage to buy their first house.
- Seniors who want to leave money to adult children who provide their care. Many adult children sacrifice time at work to care for an elderly parent who needs help. This help may also include direct financial support. Life insurance can help reimburse the adult child’s costs when the parent passes away.
- Children or young adults who want to lock in low rates. The younger and healthier you are, the lower your insurance premiums. A 20-something adult might buy a policy even without having dependents if there is an expectation to have them in the future.
- Stay-at-home spouses. Stay-at-home spouses should have life insurance as they have significant economic value based on the work they do in the home. According to Salary.com, the economic value of a stay-at-home parent would have been equivalent to an annual salary of $162,581 in 2018
- Wealthy families who expect to owe estate taxes. Life insurance can provide funds to cover the taxes and keep the full value of the estate intact.
- Families who can’t afford burial and funeral expenses. A small life insurance policy can provide funds to honor a loved one’s passing
- Businesses with key employees. If the death of a key employee, such as a CEO, would create a severe financial hardship for a firm, that firm may have an insurable interest that will allow it to purchase a life insurance policy on that employee.
- Married pensioners. Instead of choosing between a pension payout that offers a spousal benefit and one that doesn’t, pensioners can choose to accept their full pension and use some of the money to buy life insurance to benefit their spouse. This strategy is called pension maximization.
- Those with preexisting conditions. Such as cancer, diabetes, or smoking. Note, however, that some insurers may deny coverage for such individuals, or else charge very high rates.
Considerations Before Buying Life Insurance
1. Research Policy Options and Company Reviews
Because life insurance plans are a significant expense and commitment, it is vital to conduct adequate due diligence to ensure that the firm you choose has a strong track record and financial strength, especially since your heirs may not get any death benefits for many decades. Investopedia has analyzed scores of organizations that provide various types of insurance and ranked the best in multiple areas.
2. Consider How Much Death Benefit You Need –
Life insurance can hedge your bets and safeguard your loved ones if you die while the policy is active. Buying too much or insuring people whose income doesn’t need to be replaced makes less sense. The following must be considered.
What expenses wouldn’t be covered by death? If your spouse is wealthy and you have no children, it may not be necessary. Still, evaluate how your potential death would affect a spouse and how much financial help they would need to grieve without returning to work prematurely. If both partners’ income is needed to sustain a lifestyle or satisfy financial obligations, they may need separate life insurance.
3. Know Why You’re Buying Life Insurance –
Ask yourself what you’re insuring when getting a life insurance policy for a family member. Children and elderly don’t have much money to replace, but burial costs may need to be paid. A parent may choose to buy a moderate-sized coverage for their child when they’re young to preserve their insurability beyond burial costs. Doing so ensures that their child can financially secure their future family. Parental life insurance coverage for children is limited to 25% of their own policy.
Could investing permanent insurance premiums over time yield a greater return? If a major income doesn’t need to be replaced or policy investment returns on cash value are too cautious, constant saving and investing—such as self-insuring—may be a better buffer against unpredictability.
How Life Insurance Works
A life insurance policy has a death benefit and premium. While term life insurance has these two components, permanent or whole life insurance contains cash value.
- Death Benefit: Insurance companies guarantee the death benefit or face value to policy beneficiaries when the policyholder dies. Parental insurance may benefit their children. The insured will choose a death benefit based on the beneficiaries’ expected future requirements. The insurance company will decide if there is an insurable interest and if the proposed insured qualifies for coverage based on age, health, and hazardous activities.
- Premium: Insurance premiums are paid by policyholders. Premiums are based in part on the insured’s life expectancy and how probable the insurer is to pay the death benefit if the policyholder pays the premiums. The insured’s age, gender, medical history, work hazards, and high-risk hobbies affect life expectancy.
Part of the premium covers insurance company operating costs. insurance with larger death benefits, higher-risk individuals, and cash-value perpetual insurance cost more. - Cash value: Permanent life insurance cash value has two uses. The policyholder can use it as a tax-deferred savings account for the insured’s lifetime. Some regulations restrict withdrawals based on how the money is spent. For instance, the policyholder may borrow against the cash value and pay interest on the loan principal. Cash can be used to pay premiums or buy more insurance. The insurance firm keeps the cash value after the insured dies. Loans against cash value lower the policy’s death benefit.
Life Insurance Riders and Policy Changes
Many insurance firms let clients customize their policies. Riders are the most popular way policyholders can change coverage. There are numerous riders, however provider availability varies. Most policies charge more for each rider or a fee to exercise them, although some include them in their main premium.
- The accidental death benefit rider provides additional life insurance coverage in the event the insured’s death is accidental.
- The waiver of premium rider relieves the policyholder of making premium payments if the insured becomes disabled and unable to work.
- The disability income rider pays a monthly income in the event the policyholder becomes unable to work for several months or longer due to a serious illness or injury.
Upon diagnosis of terminal illness, the accelerated death benefit rider allows the insured to collect a portion or all of the death benefit. - The long-term care rider is a type of accelerated death benefit that can be used to pay for nursing-home, assisted-living, or in-home care when the insured requires help with activities of daily living, such as bathing, eating, and using the toilet.
- A guaranteed insurability rider lets the policyholder buy additional insurance at a later date without a medical review.
Borrowing Money: Most permanent life insurance has borrowable monetary value. You borrow money from the insurance company and use your cash value as collateral. In contrast to other loans, the policyholder’s credit score is irrelevant. Loan interest goes back into the policyholder’s cash value account, and repayment conditions are variable. Loans can lower insurance death benefits.
Funding retirement: Cash-value or investment policies can provide retirement income. This option may only be good for people who have maxed out other tax-advantaged savings and investment accounts due to its high costs and lesser death benefit. Life insurance can also fund retirement through pension maximization.
Qualifying for Life Insurance
Since there are hundreds of life insurance insurers, practically anyone can find an affordable coverage that satisfies at least some of their demands. US life insurance and annuity companies numbered 841 in 2018, according to the Insurance Information Institute.
Additionally, many life insurance firms offer a variety of policies and specialize on certain needs, such as chronic health policies. Specialist life insurance agents know what firms offer. A broker can help applicants locate insurance for free. If they look hard enough and are ready to pay a high price or accept a less-than-ideal death benefit, practically anyone may receive life insurance.
Usually, the insurance market is considerably larger than many customers assume, life insurance may be possible and inexpensive even if past applications have been declined or bids have been unaffordable.
Life insurance is easier to get for younger, healthier people than older, sicker people. Tobacco use and dangerous activities like skydiving make it tougher to qualify or raise premiums.
Who Needs Life Insurance?
- Age (life insurance is less expensive)
- Gender (female tends to be less expensive)
- Smoking (smoking increases premiums)
- Health (poor health can raise premiums)
- Lifestyle (risky activities can increase premiums)
- Family medical history (chronic illness in relatives can raise premiums)
- Driving record (good drivers save on premiums)
What Are the Benefits of Life Insurance?
- Payouts are tax-free. Life insurance death benefits are paid as a lump sum and are not subject to federal income tax because they are not considered income for beneficiaries.
- Dependents don’t have to worry about living expenses. Most policy calculators recommend a multiple of your gross income equal to seven to 10 years that can cover major expenses like mortgages and college tuition without the surviving spouse or children having to take out loans.
- Final expenses can be covered. Funeral expenses can be significant and can be avoided with a burial policy or with standard term or permanent life policies.
- Policies can supplement retirement savings. Permanent life policies such as whole, universal, and variable life insurance can offer cash value in addition to death benefits, which can augment other savings in retirement
How Do You Qualify for Life Insurance?
Applicants seeking life insurance must submit applications. Life insurance is offered to most. However, age, health, and lifestyle can dramatically affect premiums. Some life insurance doesn’t require medical information but has higher premiums and a waiting time before the death benefit is paid.
How Does Life Insurance Work?
Premiums buy a death benefit in life insurance. Term life insurance, a common variety, lasts 10 or 20 years. As long as premiums are paid, permanent life insurance provides a death benefit for life.
Source and for further information: Investopedia
